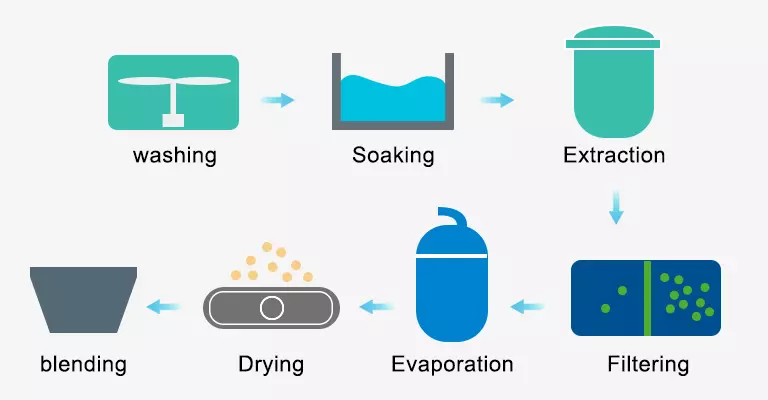
The commonly used techniques for extracting gelatin include alkali, acid and enzyme treatment. The yield and quality will be affected if there’s any mistake in these processes. Gelatin manufacture involves three main processes that are pretreatment, gelatin extraction and post stage.
In order to disintegrate the cross-links between molecules in pre-gelatin extraction, the raw material is first cleaned to remove fat and then submerged in acid, alkali, or enzyme solutions. Pretreated raw material is hydrolyzed into a water-soluble peptide by hot water during gelatin extraction, so its molecular weight reduces greatly. This step is key to the quality. The post procedure consists of the gelatin filtration, evaporation, sterilization, drying, and packaging.
What raw materials are used to produce gelatin?
Gelatin is moderate hydrolyzed and denatured collage. It dissolves in hot water. Typical raw materials for gelatin are fresh animal skins, bones, and tannery waste. These days, most gelatin is taken out of cattle or pigs. However, it’s prone to religious controversy because cows are considered holy creatures in Hindu culture while pigs are prohibited by Jews and Muslims. Bovine gelatin has been suffered greatly in recent years due to outbreaks of mad cow disease and foot-and-mouth disease. Scientific institutions claim that even if infected raw materials was entered into the manufacturing process accidentally, it’s safe because the proteins are all hydrolyzed into peptides. Nevertheless, no one wants to risk his life. Although manufacturers also employ chicken and fish, their market share is quite tiny due to high costs and scarcity of raw materials.
How is gelatin processed?

The four methods of producing gelatin are the acid, liming, enzymatic and heated under high pressure processes.
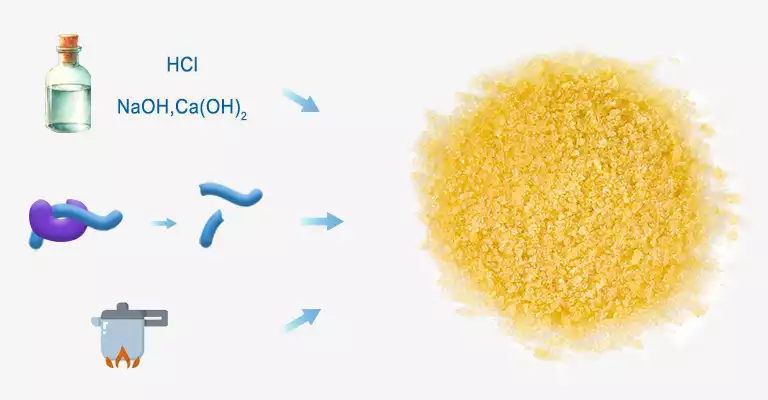
The animal skin is soaked in hydrochloric acid to hydrolyze collagen. Then, gelatin is obtained heating it in tanks. The raw material is heated about 5 times. The temperature rises by 10°C every time until it boils. Each heating lasts 4-6 hours to guarantee that collagen hydrolyzed as much as possible. The acid method is also suitable for bones that require demineralization. The Type A gelatin is produced by this method. It has an isoelectric point between PH 7-9.
Lime or sodium hydroxide can also be used as pretreatment since it cleaves chemical bonds and hydrogen bonds in collagen. Other steps resemble those for making type A gelatin. This is known as type B gelatin that has an isoelectric point of pH 4.6-5.2. This process works well with fatty materials like fresh pig skin.
Enzyme treated gelatin
Enzyme-treated gelatin production starts when trypsin or pepsin breaks down collagen covalent bond. This makes it easy to extract gelatin at subsequent process. The rest steps are identical to traditional method where the hydrogen bonds in the triple helix were broken down by heat. We call such kind of gelatin "type E."
High-pressure hydrolysis
Collagen is boiled in a pressure cooker at 140°C for 20 minutes. Then it’s filtered to get pure solution contains gelatine. This can get gelatin quickly without soaking raw materials into acid, alkali or enzyme solutions. However, it’s difficult to avoid over hydrolysis, and the product has darker color and poor quality. Therefore, it’s not used in large-scale production, but very suitable for household.