About 30% of gelatin is used in the pharmaceutical industry, most of which is used to make soft and hard capsules that are used to contain medication and dietary supplements due to several advantages.
The bitter taste and unpleasant odor of drugs are masked by capsule, and their small size and smooth gelatin shells make them easy to swallow. The capsules also isolate moisture, oxidation and microbial contamination to keep the medication stable and extend their shelf life. The light blocking agent is usually added for anti-decomposition due to light exposure.
Capsules are standardized and produced by automatic precision machines to ensure their accurate dose. They can be customized with different colors to make them more recognizable and easier to differentiate from each other. When they are treated with formaldehyde, the enteric-soluble capsules are achieved. They are insoluble in stomach to avoid some drugs being degraded by gastric juice or irritating the stomach.
Hard Capsule/double-piece capsule💊
The hard capsules are also called two-piece capsules. They consist of two cylindrical shells: a smaller diameter and longer “body” that contains powdered ingredients or miniature pellets and is sealed by “cap”. The production and filling of hard capsules is usually done by different companies. Modern hard capsules are produced by the dipping method. The neatly arranged steel pins are dipped into gelatin solution and then pulled out. After the solution dries, gelatin shells are cut and stripped off to get the two halves of capsules. Then these hard capsules are sold as closed units to pharmaceutical plants and separated before filling.
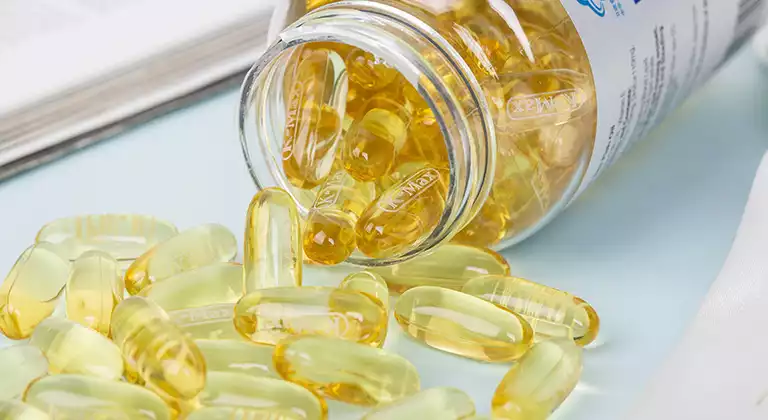

Softgel/one-piece capsule💊
The soft capsules are also called single-piece capsules. They consist of a continuous oval shaped gelatin shell and internal filler. Their shells are soft and elastic, as plasticizers such as glycerin or sorbitol are added to decrease hardness. They are commonly used to hold liquid or semi-liquid medications whose active ingredients are dissolved or suspended in oil, such as fat-soluble vitamins. Unlike hard capsules, most modern soft capsules are produced by the automatic rotary dies method, where the shell making and drug filling are done at the same time.